Page 22 - REBRAME - Revista Brasileira de Medicina de Emergência
P. 22
Gaspardi AC, Fujita Neto FG
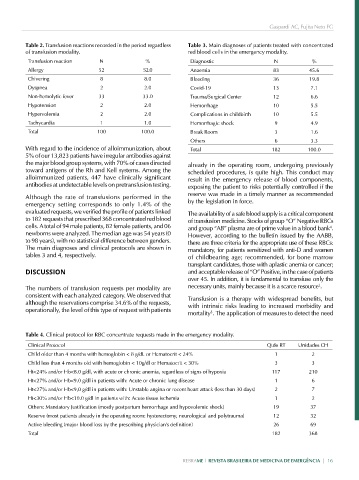
Table 2. Transfusion reactions recorded in the period regardless Table 3. Main diagnoses of patients treated with concentrated
of transfusion modality. red blood cells in the emergency modality.
Transfusion reaction N % Diagnostic N %
Allergy 52 52.0 Anaemia 83 45.6
Chivering 8 8.0 Bleeding 36 19.8
Dyspnea 2 2.0 Covid-19 13 7.1
Non-hemolytic fever 33 33.0 Trauma/Surgical Center 12 6.6
Hypotension 2 2.0 Hemorrhage 10 5.5
Hypervolemia 2 2.0 Complications in childbirth 10 5.5
Tachycardia 1 1.0 Hemorrhagic shock 9 4.9
Total 100 100.0 Break Room 3 1.6
Others 6 3.3
With regard to the incidence of alloimmunization, about Total 182 100.0
5% of our 13,823 patients have irregular antibodies against
the major blood group systems, with 70% of cases directed already in the operating room, undergoing previously
toward antigens of the Rh and Kell systems. Among the scheduled procedures, is quite high. This conduct may
alloimmunized patients, 447 have clinically significant result in the emergency release of blood components,
antibodies at undetectable levels on pretransfusion testing. exposing the patient to risks potentially controlled if the
reserve was made in a timely manner as recommended
Although the rate of transfusions performed in the
emergency setting corresponds to only 1.4% of the by the legislation in force.
evaluated requests, we verified the profile of patients linked The availability of a safe blood supply is a critical component
to 182 requests that prescribed 368 concentrated red blood of transfusion medicine. Stocks of group “O” Negative RBCs
cells. A total of 94 male patients, 82 female patients, and 06 and group “AB” plasma are of prime value in a blood bank .
4
newborns were analyzed. The median age was 54 years (0 However, according to the bulletin issued by the AABB,
to 98 years), with no statistical difference between genders. there are three criteria for the appropriate use of these RBCs:
The main diagnoses and clinical protocols are shown in mandatory, for patients sensitized with anti-D and women
tables 3 and 4, respectively. of childbearing age; recommended, for bone marrow
transplant candidates, those with aplastic anemia or cancer;
DISCUSSION and acceptable release of “O” Positive, in the case of patients
over 45. In addition, it is fundamental to transfuse only the
2
The numbers of transfusion requests per modality are necessary units, mainly because it is a scarce resource .
consistent with each analyzed category. We observed that Transfusion is a therapy with widespread benefits, but
although the reservations comprise 34.6% of the requests, with intrinsic risks leading to increased morbidity and
operationally, the level of this type of request with patients
5
mortality . The application of measures to detect the need
Table 4. Clinical protocol for RBC concentrate requests made in the emergency modality.
Clinical Protocol Qtde RT Unidades CH
Child older than 4 months with hemoglobin < 8 g/dL or Hematocrit < 24% 1 2
Child less than 4 months old with hemoglobin < 10g/dl or Hematocrit < 30% 3 3
Ht<24% and/or Hb<8.0 g/dl, with acute or chronic anemia, regardless of signs of hypoxia 117 210
Ht<27% and/or Hb<9.0 g/dl in patients with: Acute or chronic lung disease 1 6
Ht<27% and/or Hb<9,0 g/dl in patients with: Unstable angina or recent heart attack (less than 30 days) 2 7
Ht<30% and/or Hb<10.0 g/dl in patients with: Acute tissue ischemia 1 2
Others: Mandatory Justification (mostly postpartum hemorrhage and hypovolemic shock) 19 37
Reserve (most patients already in the operating room: hysterectomy, neurological and polytrauma) 12 32
Active bleeding (major blood loss by the prescribing physician's definition) 26 69
Total 182 368
REBRAME | REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE MEDICINA DE EMERGÊNCIA | 16